Neural radiance fields (NeRF) achieve impressive performance in novel view synthesis when trained on only single sequence data. However, leveraging multiple sequences captured by different cameras at different times is essential for better reconstruction performance. Multi-sequence data takes two main challenges: appearance variation due to different lighting conditions and non-static objects like pedestrians. To address these issues, we propose NeRF-MS, a novel approach to training NeRF with multi-sequence data. Specifically, we utilize a triplet loss to regularize the distribution of per-image appearance code, which leads to better high-frequency texture and consistent appearance, such as specular reflections. Then, we explicitly model non-static objects to reduce floaters. Extensive results demonstrate that NeRF-MS not only outperforms state-of-the-art view synthesis methods on outdoor and synthetic scenes, but also achieves 3D consistent rendering and robust appearance controlling.
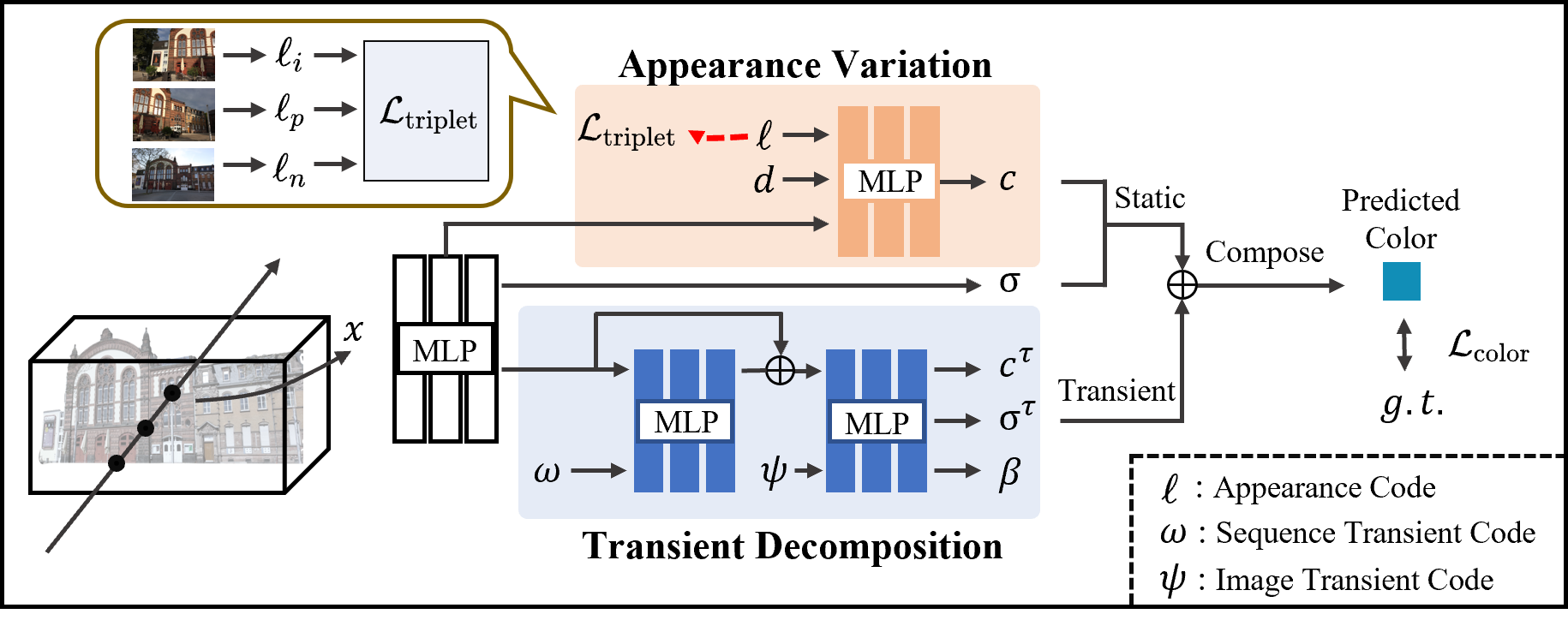
Pipeline
Our appearance variation module outputs the static color based on the per-image appearance code. We use triplet loss to regularize the distribution of appearance code. By utilizing the image transient code and sequence transient code, the transient decomposition module can effectively generate the color, density, and uncertainty for non-static objects. The static and transient components are then integrated to obtain the pixel's color and uncertainty. Finally, we employ a color loss to supervise the radiance field.
Ablation
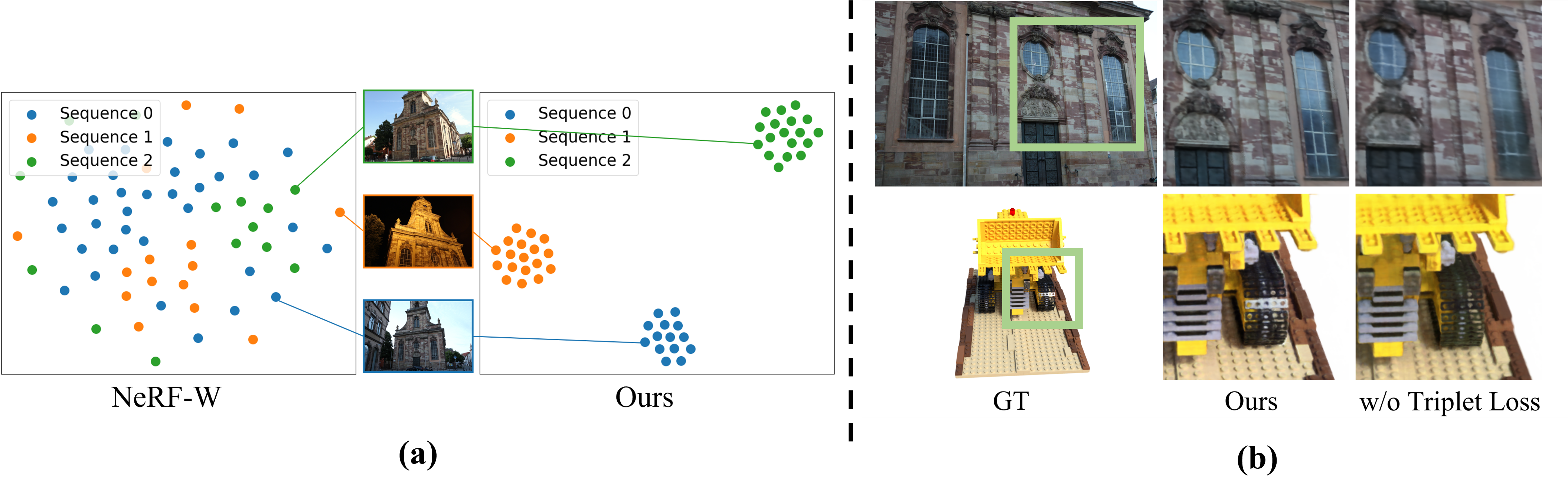
(a) Without triplet loss, the appearance codes from different sequences are overlapped due to overfitting. (b) Our method can reconstruct fine details (window dividers) and 3D consistent reflection (on windows and bulldozer tracks) by utilizing triplet loss to prevent appearance code overfitting.

In the provided GT diagram, we label sequence transient region as yellow and image transient region as green. Subsequently, we present the decomposition performance of various algorithms alongside their corresponding depth maps. Our proposed method addresses the challenging yellow region that SOTA methods struggle with, but also preserves the intricate geometric details of the static region, resulting in more accurate depth estimation.
Results

Our method significantly improves the rendering performance in test views with multiple sequences as training data. What's more, we achieve robust appearance interpolation as below:
